CTC application teams can gradually evolve their environment segregation maturity, transitioning from ad-hoc practices to self-service. This roadmap ensures a systematic and controlled approach to enhance segregation capabilities, leading to improved efficiency, agility, and quality in software development and testing processes. Environment maturity in segregation refers to the level of sophistication and effectiveness in segregating different types of test environments. A higher maturity level indicates a more advanced and refined approach to environment segregation, ensuring better control, isolation, and efficiency. Here are different levels of environmental maturity in segregation:
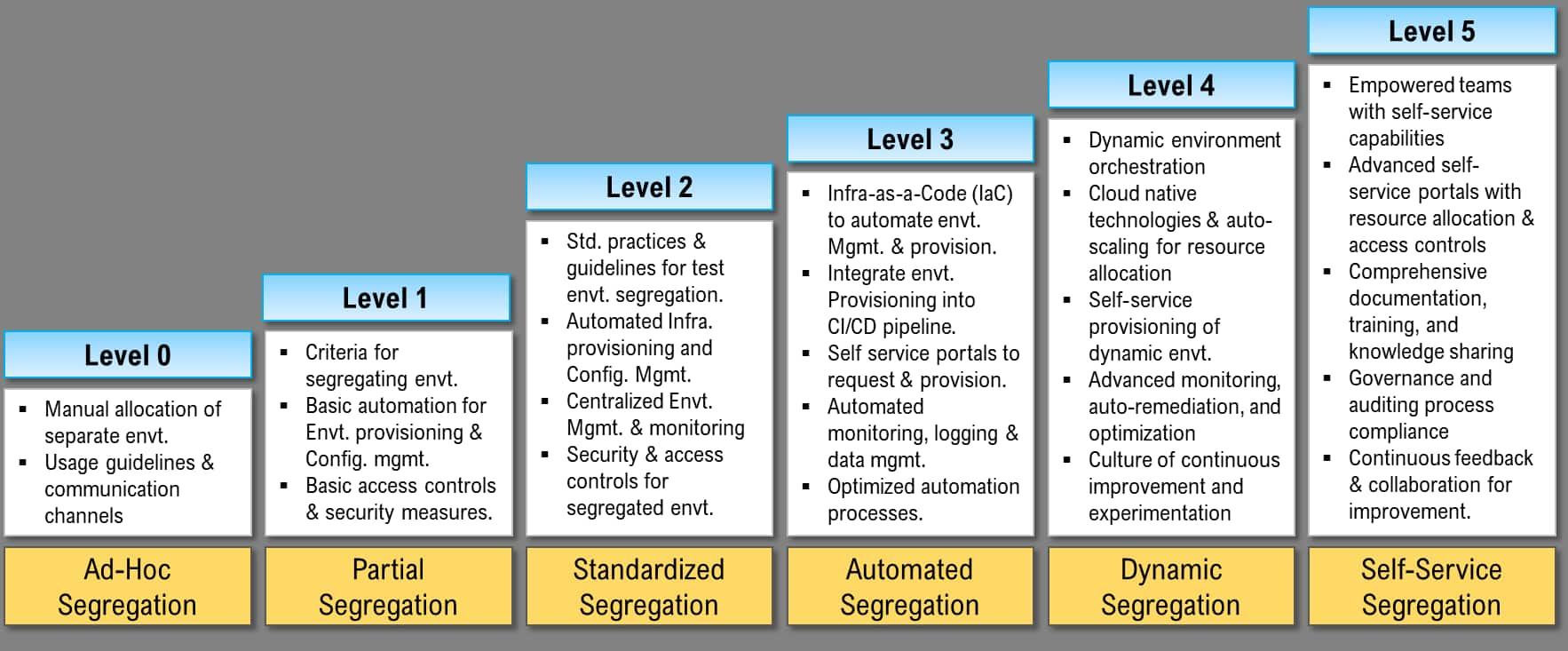
Level of Environment Segregation Maturity
Level 0: Ad-hoc Segregation
Implement basic segregation by manually allocating separate environments for different teams or projects.
Develop guidelines and communication channels to coordinate environment usage.
Level 1: Partial Segregation
Define clear criteria for segregating environments based on specific requirements, projects, or teams.
Implement basic automation for environment provisioning and configuration management.
Establish basic access controls and security measures.
Level 2: Standardized Segregation
Establish standardized practices and guidelines for segregating test environments.
Automate infrastructure provisioning and configuration management using tools like Terraform and configuration management systems.
Implement centralized environment management and monitoring.
Enhance security and access controls for segregated environments.
Level 3: Automated Segregation
Leverage infrastructure-as-code (IaC) principles to automate environment provisioning and management.
Integrate environment provisioning into the CI/CD pipeline.
Implement self-service portals for teams to request and provision their segregated environments.
Implement automated monitoring, logging, and data management mechanisms.
Continuously optimize automation processes for improved efficiency.
Level 4: Dynamic Segregation
Implement dynamic environment orchestration using containerization technologies like Kubernetes or Docker Swarm.
Leverage cloud-native technologies and auto-scaling mechanisms for resource allocation.
Enable self-service provisioning of dynamic environments based on demand.
Implement advanced monitoring, auto-remediation, and optimization mechanisms.
Foster a culture of continuous improvement and experimentation.
Level 5: Self-Service Segregation
Empower teams with self-service capabilities to provision and manage their own segregated environments.
Implement advanced self-service portals or interfaces with resource allocation and access controls.
Establish comprehensive documentation, training, and knowledge sharing practices.
Implement governance and auditing processes to ensure compliance.
Continuously seek feedback and collaborate across teams for ongoing improvement.





