Overview :
Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including retail. Canadian Tire, being a prominent retailer in Canada, could benefit from incorporating generative AI into its operations.
Gen AI can be used to provide personalized recommendations, optimize inventory management, develop virtual shopping assistants, generate new product designs, and detect fraud. These applications can enhance the customer experience, improve operational efficiency, and drive innovation in the retail industry.
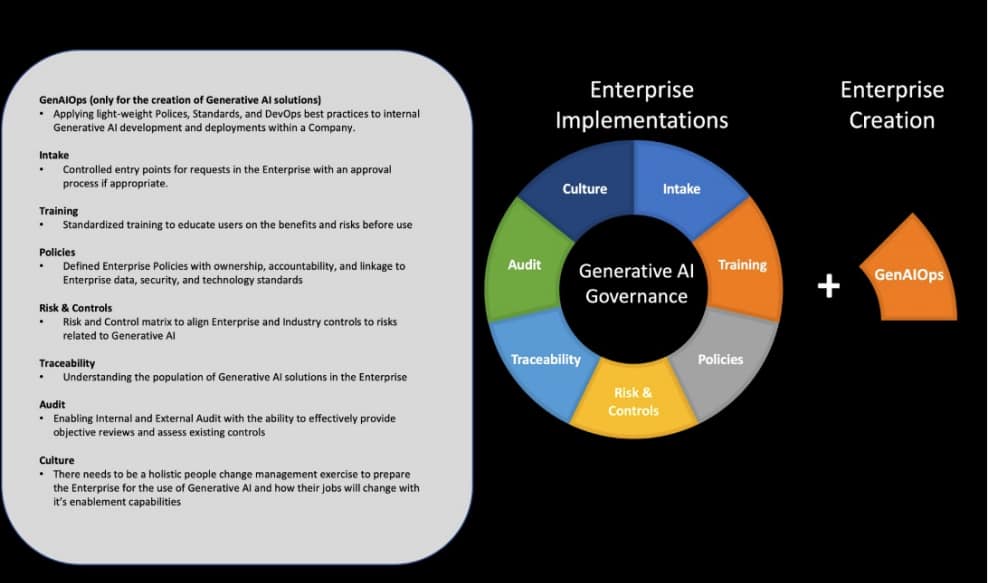
There are several considerations which will be important for adoption:
- Most of the Enterprise Implementation items will already exist in an Enterprise so they should be leveraged when possible.
- Generative AI will soon be ubiquitous in every aspect of the Enterprise so Governance will need to be an enabler and allow for growth - but with guardrails.
- Layered approach to Governance for Deployment of services and Creation of new solutions
- Start with the basics of Governance and build from there
- There is no "one size fits all" Governance and your Framework will need to change over time
- Provide Risk Management and Audit groups a baseline of what the "ideal state" looks like
- Invest in your teams with Education and Coaching
- Provide enough Risk Coverage to help the Enterprise understand how their Risk Appetite is affected
GenAI Technology Standard
| Policy Domain | Domain Details |
|---|---|
| Policy Statement | Generative AI is becoming an ubiquitous technology within Business and Technology, and it is the policy of the Enterprise to protect all company data and development assets, as well as customer information, from exposure that would violate regulatory requirements and the Enterprise Risk Appetite during the Development, Testing, and Deployment of GenAI solutions.
|
| Policy Context | Internal Generative AI development and deployments that are created within the Enterprise - leveraing tools, services, and models provided from internal or external sources.
|
| Development & Operations Responsibilities | All Development and Operations staff are responsible for protecting corporate and customer data and information during GenAI development. Details on appropirate tools, services, APIs, Open Source resources which are found in the GenAI Technology Standard, will be followed.
|
| Risk and Audit Responsibilities | Risk, Governance, and Internal Audit will perform periodic reviews of GenAI development solutions that are holistic and included all phases of the software lifecycle - including Production monitoring and retraining of relevant models.
|
| Multi-Disciplinary Teams Responsibilities | Teams such as HR and Legal will need to be informed of Generative AI development within an Enterprise for legal considerations as well as HR onboarding and training requirements for relevant employees. |
| Owner | Enterprise Owner (will vary for each Enterprise)
|
| Standard Domain | Domain Details |
|---|---|
| Description of Standard | While there are standards being created to address the users of consumer generative AI services, this standard is focused on providing mandatory guardrails and requirements to support an Enterprise's Policy for internal Development, Testing, and Deployment of Generative AI solutions.
|
| Standard Specification | All internal Development of Generative AI services and applications will adopt the following guardrails and requirements:
|
| Where to Apply This Standard | This standard applies to all Development and Delivery teams within the Enterprise - including external developers and engineers who are working on proprietary applications and services.
|
| Owner | Enterprise Owner (will vary for each Enterprise)
|
| Standard Terms | Description |
|---|---|
| Generative AI (GenAI) | Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence technology that can produce various types of content, including text, imagery, audio and synthetic data. (techtarget.com)
|
| Large Language Models (LLM) | A large language model, or LLM, is a deep learning algorithm that can recognize, summarize, translate, predict and generate text and other content based on knowledge gained from massive datasets. (nvidia.com)
|
| Retrieval Augmented Generation | RAG retrieves data from outside the language model and augments the prompts by adding the relevant retrieved data in context (AWS)
|
| AI Hallucinations | When an AI is perceiving something that is not real.
|
| Standard Servies & Tools Review Topics | Description |
|---|---|
| Review Context | To help enable Enterprises with onboarding of Services and Tools, the following topics could be leveraged as a checklist to help streamline governance and security reviews by providing a baseline set of criteria.
|
| Enterprise Cloud Provider | Cloud Provider's such as AWS and Azure have started releasing Generative AI tools, APIs, and Services (GenAI Development as a Service for example) such as Azure Promptflow and Amazon Kendra. If the Enterprise preferred Cloud Provider provided Generative AI development tooling, it may be easier to have the service or tool certified for Enterprise use.
|
| Service Certification | An Enterprise may already have a process in place to Certify Cloud services or tooling with existing checklists for common topics such as security, traceability, audit, logging, and etc. Tools such as Azure Promptflow or Amazon Kendra could also be onboarded leveraging existing processes like this - providing Governance decision makers with criteria and review topices they are familiar with.
|
| Open Source Maturity | If the Enterprise has an existing Open Source Program Office and is comfortable with the use of Open Source tooling, leveraging Generative AI Open Source services and tools should follow existing processes. But, for an Enterprise that does not currently have governance and management in place for Open Source tools, the overhead of onboarding new tools available in the Open Source community may be too time consuming. Tools provided by preferred Cloud Providers may be a better option until Open Source maturity has increased.
|
| Enterprise Industry | An Enterprise security stance and risk appetite will be driven by its Industry. For example, Financial Institutions, Retail, Insurance, and Health Care companies all have different regulations and requirements that drive all of their decisions regarding services and tools. When making a decision on Generative AI development services and tools, its important to consider what regulations or requirements will need to be followed. For example. if an Enterprise is developing a Generative AI application for processes that are related to financial reporting, they may need to consider the controls that will be reviewed as part of a SOX Audit. However, if the Enterprise process is not related to requlations or requirements, there will be more lenient controls and security controls.
|
| Data Classification | Any decisions on services or tooling that will be leveraged for Generative AI development should factor in the classification of the data that will be leveraged by the Language Models. Data controls and governance for restricted or confidential data are much more strict than internal or public data.
|
| Data Residency | There are data residency requirements for regions around the World which need to be considered for Generative AI development. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation requires personal data for EU residents needs to stay in the EU. This is an important consideration for Open Source tools or other Services that may be sending data to other regions around the world.
|
| Enterprise Risk Appetite | The Enterprise Risk Appetite is the amount of risk an Enterprise is willing to take on to meet its objectives. This is an important factor for Generative AI development since its such a game-changer for the Industry. An Enterprise who has bee traditionally conservative may update their Risk Appetite to take advantage of the tremendous potential of Generative AI Capabilities.
|
GenAI Tech Standard Responsible AI Principles Alignment – GitHub Copilot Example
| Principle | Y/N | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Privacy And Data Protection | Y | GitHub Copilot prompts are discarded once a suggestion is returned and suggestions are not retained by GitHub. GitHub Copilot does not use Prompts or Suggestions to train AI models. These inputs are not retained or utilized in the training process of AI models for GitHub Copilot. User engagement data is usage information about events generated when interacting with a code editor. These events include user edit actions (for example completions accepted and dismissed), error messages, and general usage data to identify user metrics such as latency and feature engagement. |
Responsible Data Use |
Y | As mentioned above, GitHub Copilot does not use Prompts or Suggestions to train the AI Models and prompts are discarded immediately once a suggestion is returned. As part of Microsoft and GitHub’s ongoing commitment to responsible AI, GitHub and Microsoft extends their IP indemnity and protection support to their customers who are empowering their teams with GitHub Copilot. |
| Fairness Transparency and Accountability | Y | GitHub Copilot is not a substitute for developers. In fact, it empowers them to be more productive, accelerating some coding tasks to free up time for them to focus on more important problems. Early research on generative AI and GitHub Copilot specifically find that these tools have the potential to lower barriers to entry and enable more people to become software developers. |
| Accuracy, Reliability, and Human Oversight | Y | Traditional Software Development best practices, such as Code Reviews, Testing, and Security Scans, still apply and provide the Human Oversight that is expected with all software Delivery. |
| Customer Autonomy | Y | Developers using GitHub Copilot have the choice whether to accept the Generative AI prompt and suggestions or not. It’s designed to act as an AI-pair programmer and not as a replacement for the developer. |
| Continuous Improvement and Stakeholder Engagement | Y | GitHub Copilot is continuously improving based on customer feedback and investment from Microsoft and GitHub. |









