Purpose
Canadian Tire Corporation is modernizing the application portfolio and migrating from on-prem servers to the cloud. The purpose of this document is to outline the testing approach, types of testing, tools, and test considerations for the cloud migration.
Target Audience
QE Chapter Leader, QE Architect, QE Specialist (Functional SME), Test Automation Engineer (TAE), Performance Test Engineer (PTE), Security Test Engineer (STE), Accessibility Test Engineer (ATE), Test Environment Specialist and Test Data Architect.
Definition
Cloud migration testing ensures the application continues to perform as it should after it moves to the cloud environment and provides a better user experience. Cloud computing as a model offers services over the internet, and many users share the same services, so there is a need to ensure performance and security. In addition, functionality against the requirements in the new platform and the correctness and completeness of the migrated DB needs to be validated.
Objectives
The following are the various types of strategies that the organization can adopt for migrating applications to the cloud.
Retain
- The application functionalities will be retained in the cloud platform.
Rehost
- Clone and move the application onto a new infrastructure
Replatform
- Re-use the existing architecture and application code asset in the cloud platform
Replace/Rearchitect/Refactor
- Transform legacy application to meet defined requirements in the Cloud, customization of cloud features & Database remediation
Testing Approach
Testing for cloud migration consists of the following phases:
Pre-Migration testing
- In this phase, the QE team performs functional, system and integration, performance, and security testing etc. in the existing on-premise environment to ensure critical business functionalities are working as expected, capture current performance benchmarks, and uncover any known security vulnerabilities before migration.
Post-Migration testing
- The QE teams perform infrastructure/server build QA validation, data/ETL migration testing, functional, system and integration, and performance testing to ensure business functionalities work fine in the cloud environment after migration. The team also conducts security testing such as authentication, authorization, and vulnerability scans to identify and address vulnerabilities in the cloud environment.
An illustrative view of the various types of testing that are conducted as part of cloud migration testing is shown below.
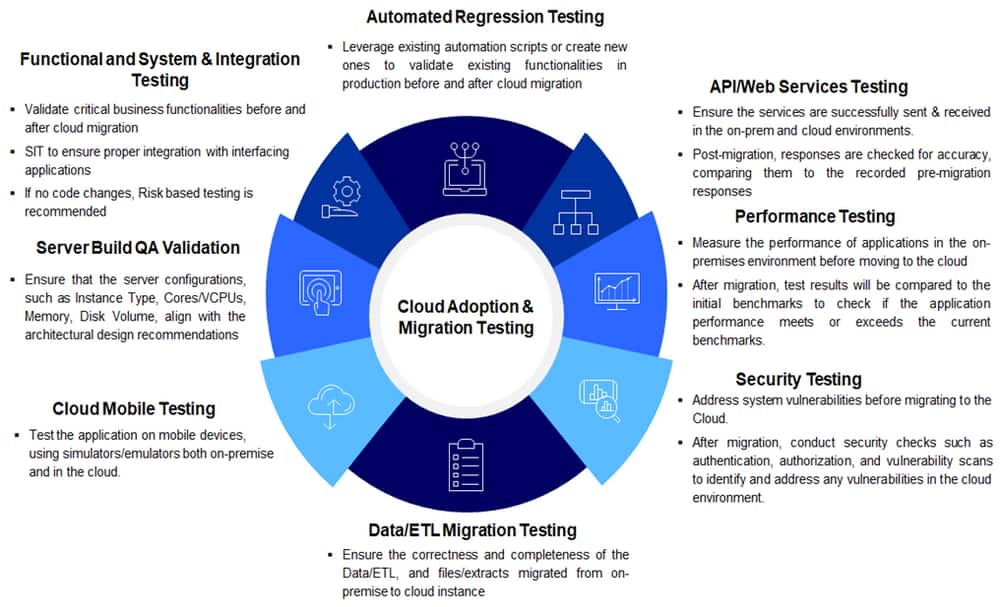
Types of Testing – Detailed View
The QE team will perform the following tests in the pre-migration and post-migration testing phases and compare and report the test results for the applications in on-premise and cloud environments.
Refer to the links below to understand the following testing types.
| Testing Type | Reference Link |
|---|---|
Functional and System & Integration Testing |
Functional and SIT - Risk Based Testing – |
Automated Regression Testing |
Regression Testing- Test Automation- |
Performance Testing |
Besides the testing mentioned in the above table, the QE team will also perform the following types of testing as part of the cloud migration testing.
API/Web Services Testing
The test aims to ensure the successful sending and receiving of API/Web Services in on-premises and cloud environments.
The team will use a testing tool to create and run test scripts on the current environment for benchmarking.
Scripts used in the pre-migration phase will be modified to work in the cloud environment.
Post-migration, API/Web Services Responses are checked for accuracy, comparing them to the recorded pre-migration responses.
Data/ETL Migration Testing
The QE team will perform Data/ETL migration testing to ensure the correctness and completeness of the Data/ETL and files/extracts migrated from on-premise to cloud instance. The key aspects that will be validated as part of this testing are:
Data Model Validation
- The data model in cloud DB will be verified and validated against the On-Premise DB to ensure no anomalies.
Data Validation Checks
- Validation of in-scope tables for which data got migrated from on-premise to Cloud database instance would be performed by comparing the record count and column-by-column table data.
Data Integrity Checks
- Referential Integrity and Duplicate Checks will be done on cloud database instance tables.
Cloud Mobile Testing
This testing aims to test the application on mobile devices, using simulators/emulators on-premise and in the cloud environment.
It includes functional testing, compatibility testing, screen validation, and mobile-specific validation, such as network availability, call handling, and memory availability.
Test results from both on-premise and cloud environments are analyzed, and any deviations are identified and fixed as defects.
Server Build QA Validation
The QE/Infrastructure team will check the server build of all the servers moved to the cloud.
They will ensure that the server configurations, such as Instance Type, Cores/VCPUs, Memory, and Disk Volume, align with the architectural design recommendations.
After passing QE validation, the servers will be configured and deployed on the cloud environment.
Security Testing
Authentication
- involves verifying identities, tracing origins, ensuring product legitimacy, and confirming trustworthy computer programs.
Authorization
- determines if a requester has permission to receive a service or perform an operation. The application will be analyzed to identify potential threats and attacks in each business/data flow and critical areas. Access control specifications and security requirements will be reviewed.
Code Reviews
- vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing to benchmark against industry standards like OWASP, SANS, and coding flaws.
Collaboration
- The security testing team will collaborate with the project team to identify and address the vulnerabilities before the release is deployed to production.
Cloud Migration Testing Process Flow
The Testing activities for cloud migration will align with the Agile STLC model followed in CTC. The diagram below captures the migration testing activities in the testing lifecycle.
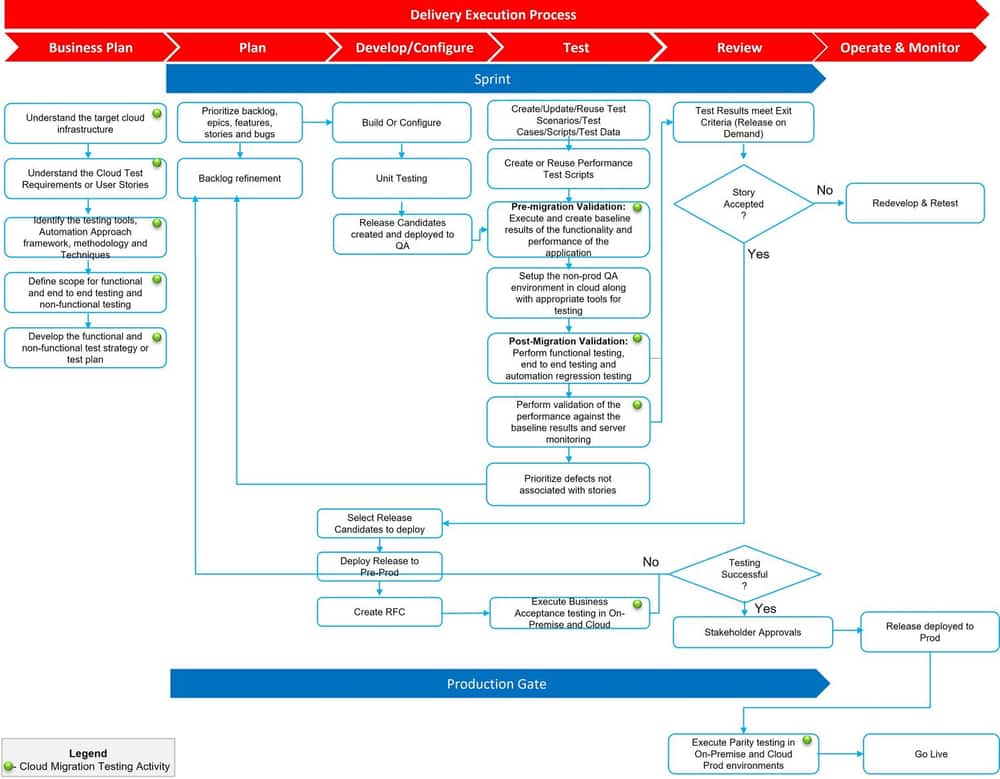
Tools/Technology
The following tools are to be considered for Cloud Migration testing:
| Testing Type | Tools |
|---|---|
Automation |
UTAF framework |
API/Web Services Testing |
Postman |
Performance Load Testing |
BlazeMeter |
Performance Monitoring |
New Relic |
Security Testing and Vulnerability Scanning |
Veracode |
Cloud Mobile Testing |
Appium |
Test & Defect Management |
Qtest JIRA |




