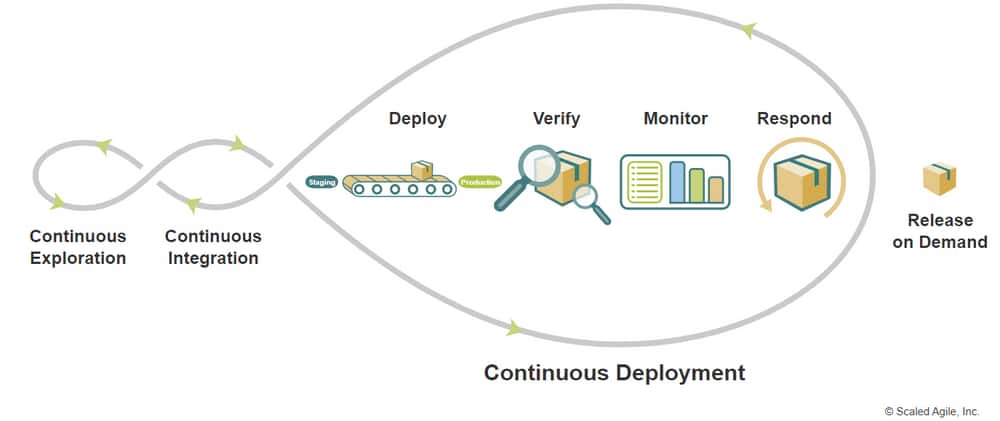
Overview
Continuous Deployment (CD) is an aspect of the Continuous Delivery Pipeline that automates the migration of new functionality from a staging environment to production, where it is made available for release.
The capability to continuously deploy is critical for releasing on demand. In turn, it allows Agile Release Train (ARTs) to respond to market opportunities with the highest possible value in the shortest sustainable lead time, permitting customers to consume new functionality when they are ready.
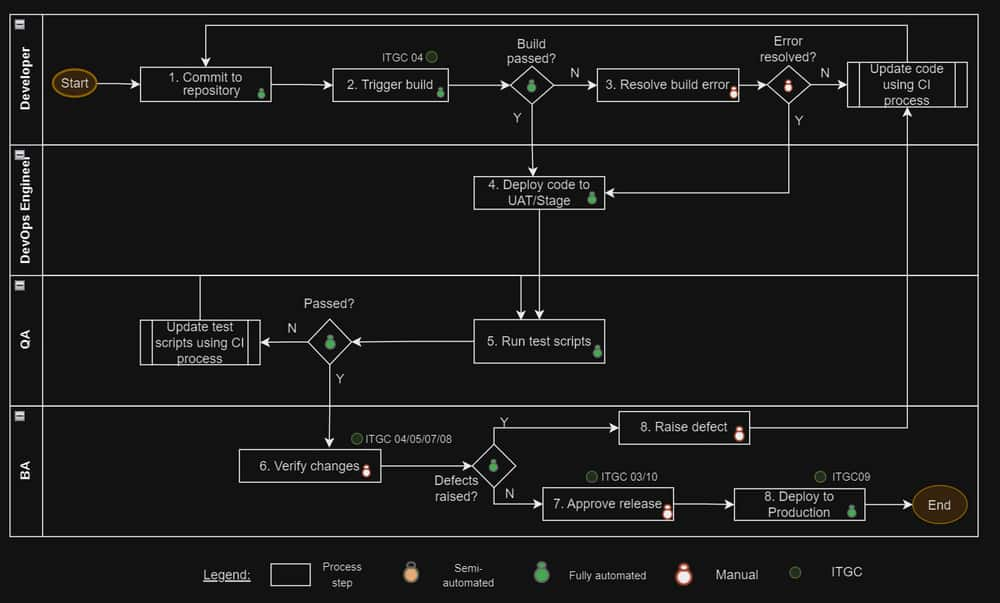
| Control Id | Control Description | Coverage in CD |
|---|---|---|
ITGC03.Development Methodology |
The organization has a solution development methodology that contains a set of requirements, which includes security and processing integrity controls, that are adhered to throughout the solution development lifecycle.
|
|
ITGC04.Application Controls |
The solution development methodology through architectural and security practices includes requirements that information systems are designed with to include application controls that support complete, accurate, authorized and valid transaction processing. Control activities:
|
|
ITGC05.User Involvement |
The enterprise has a solution development methodology that defines and maintains business functional and technical requirements that are endorsed by all stakeholders. Control activities:
|
|
ITGC09.Promotion to Production |
A process is established to restrict access to authorized individuals functions only for the migration of accepted solutions/software releases into production.
|
|
ITGC10.Testing Strategy |
A test strategy must be followed which includes testing scope, goals, approach, tools, roles, environments, test exit criteria and timing of test activities. It takes into consideration testing requirements including security, architectural design, internal controls and privacy.
|
|




